The Alarming Rise of Physician Burnout Rates: Causes, Consequences, and Solutions
Physician burnout is a growing crisis within the healthcare industry, with significant implications for both doctors and patients. Understanding the causes and consequences of increasing physician burnout rates is crucial for developing effective solutions. This article delves into the multifaceted issue of physician burnout rates, exploring its prevalence, underlying factors, impact on healthcare quality, and potential strategies for mitigation. The rising physician burnout rates represent a serious challenge that demands immediate attention and comprehensive action.
Understanding Physician Burnout
Physician burnout is characterized by three key dimensions: emotional exhaustion, depersonalization (or cynicism), and a diminished sense of personal accomplishment. Emotional exhaustion refers to feeling drained and depleted of emotional resources. Depersonalization involves developing a negative, detached, and cynical attitude towards patients and their work. Reduced personal accomplishment manifests as a feeling of incompetence and a lack of satisfaction with one’s achievements. These three dimensions intertwine to create a state of profound distress that can severely impact a physician’s well-being and professional performance.
Prevalence of Physician Burnout
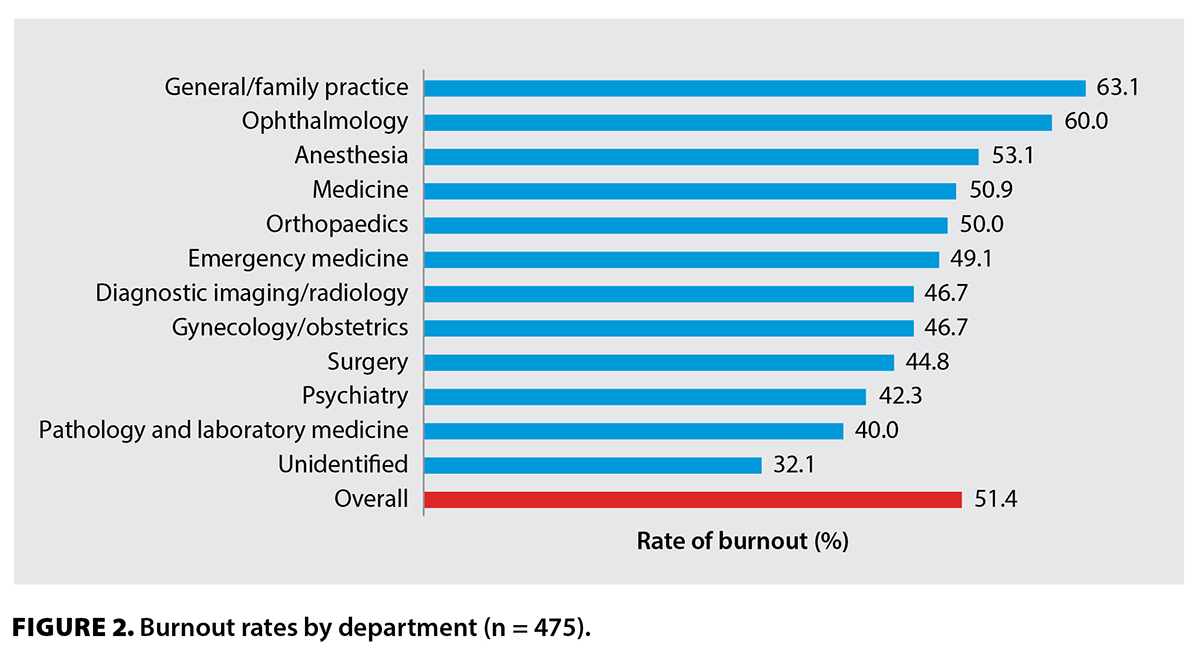
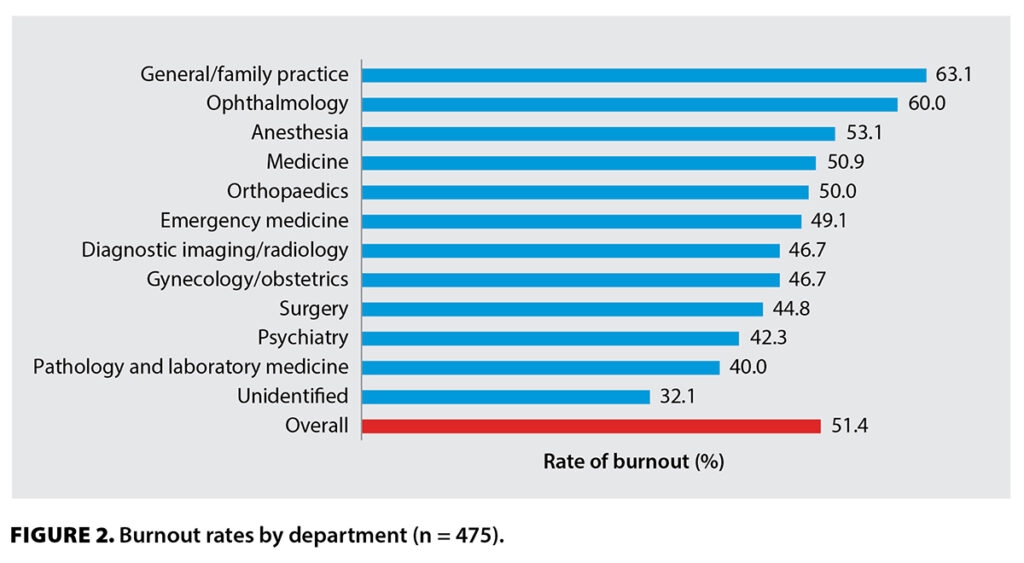
Studies consistently reveal alarming physician burnout rates across various specialties and practice settings. A 2023 Mayo Clinic study found that over 50% of physicians report experiencing at least one symptom of burnout. This prevalence is significantly higher than in other professions, highlighting the unique stressors faced by healthcare professionals. Certain specialties, such as emergency medicine, critical care, and primary care, often exhibit even higher burnout rates due to demanding workloads and high-pressure environments.
Contributing Factors to Burnout
Several factors contribute to the rising physician burnout rates. These can be broadly categorized into systemic issues, organizational factors, and individual characteristics.
- Systemic Issues: These include increasing administrative burdens, regulatory requirements, and the complexities of the healthcare system itself. Electronic health records (EHRs), while intended to improve efficiency, often add to the workload and contribute to frustration.
- Organizational Factors: Heavy workloads, long hours, inadequate staffing, and a lack of control over one’s work environment are significant contributors. A culture of overwork and a lack of support from leadership can exacerbate these issues. [See also: Improving Healthcare Work Environments]
- Individual Characteristics: Perfectionism, a strong sense of responsibility, and difficulty setting boundaries can make physicians more vulnerable to burnout. These personality traits, while often beneficial in a medical career, can become detrimental when combined with the stressors of the job.
Consequences of Physician Burnout
The consequences of physician burnout rates extend far beyond the individual physician, impacting patient care, healthcare organizations, and the overall healthcare system.
Impact on Patient Care
Burnout can negatively affect the quality of patient care in several ways. Studies have shown that burned-out physicians are more likely to make medical errors, provide suboptimal care, and exhibit decreased empathy towards patients. This can lead to reduced patient satisfaction, poorer health outcomes, and increased risk of adverse events. The increasing physician burnout rates are directly correlated with a decline in the quality of healthcare delivery.
Impact on Healthcare Organizations
Healthcare organizations also suffer from the consequences of physician burnout rates. Burnout is associated with increased physician turnover, absenteeism, and reduced productivity. Replacing physicians is costly and disruptive, and it can strain the remaining staff. Moreover, a burned-out workforce can negatively impact the organization’s reputation and ability to attract and retain top talent. [See also: The Cost of Physician Turnover] The financial and operational implications of high physician burnout rates are substantial.
Impact on Physicians’ Well-being
Burnout takes a significant toll on physicians’ personal well-being. It is linked to increased rates of depression, anxiety, substance abuse, and suicidal ideation. Burned-out physicians may experience relationship problems, social isolation, and a diminished quality of life. The emotional and psychological consequences of high physician burnout rates are devastating and demand urgent attention.
Strategies for Mitigating Physician Burnout
Addressing the rising physician burnout rates requires a multifaceted approach that targets both systemic and individual factors. Healthcare organizations, policymakers, and individual physicians all have a role to play in implementing effective solutions.
Organizational Strategies
Healthcare organizations can implement several strategies to reduce physician burnout rates:
- Reduce Administrative Burden: Streamlining administrative processes, reducing paperwork, and optimizing EHR systems can alleviate some of the burden on physicians.
- Improve Work-Life Balance: Implementing flexible scheduling options, providing adequate staffing, and promoting a culture that values work-life balance can help physicians better manage their time and responsibilities.
- Provide Support and Resources: Offering access to mental health services, peer support groups, and wellness programs can help physicians cope with stress and build resilience.
- Foster a Positive Work Environment: Creating a supportive and collaborative work environment where physicians feel valued and appreciated can improve morale and reduce burnout. [See also: Building a Supportive Healthcare Culture]
- Empower Physicians: Giving physicians more control over their work environment and decision-making processes can increase their sense of autonomy and reduce feelings of powerlessness.
Individual Strategies
Individual physicians can also take steps to mitigate burnout:
- Practice Self-Care: Engaging in activities that promote physical and emotional well-being, such as exercise, mindfulness, and hobbies, can help reduce stress and improve resilience.
- Set Boundaries: Learning to say no to additional responsibilities and setting clear boundaries between work and personal life can prevent overcommitment and exhaustion.
- Seek Support: Talking to colleagues, friends, or family members about their experiences and feelings can provide valuable support and perspective.
- Develop Coping Skills: Learning effective coping strategies for managing stress, such as relaxation techniques and cognitive restructuring, can help physicians better handle challenging situations.
- Prioritize Sleep: Ensuring adequate sleep is crucial for maintaining physical and mental health and preventing burnout.
Policy and System-Level Changes
Addressing the systemic issues contributing to physician burnout rates requires policy and system-level changes:
- Reduce Regulatory Burdens: Streamlining regulations and reducing unnecessary administrative requirements can alleviate some of the pressure on physicians.
- Improve EHR Usability: Working to improve the usability and efficiency of EHR systems can reduce frustration and improve workflow.
- Promote Mental Health Awareness: Raising awareness of mental health issues and reducing stigma can encourage physicians to seek help when they need it.
- Invest in Research: Funding research to better understand the causes and consequences of physician burnout rates and to develop effective interventions is essential.
The Future of Physician Well-being
Addressing the rising physician burnout rates is not just a matter of improving individual well-being; it is essential for ensuring the sustainability of the healthcare system. By implementing comprehensive strategies that target systemic, organizational, and individual factors, we can create a healthier and more supportive environment for physicians, ultimately leading to better patient care and a more resilient healthcare workforce. The increasing physician burnout rates demand a proactive and collaborative approach from all stakeholders to ensure a brighter future for healthcare professionals and the patients they serve. Failing to address these physician burnout rates will have dire consequences. Understanding the factors that contribute to physician burnout rates is the first step towards creating effective change. The current physician burnout rates are unsustainable. The need to address physician burnout rates has never been greater. Without intervention, physician burnout rates will continue to rise. The impact of physician burnout rates on patient care is undeniable. High physician burnout rates are a symptom of a larger problem within the healthcare system. Addressing physician burnout rates requires a holistic approach. The increasing physician burnout rates should be a wake-up call for the healthcare industry. We must act now to reduce physician burnout rates. The consequences of ignoring physician burnout rates are too great to ignore.