Decoding Medical Billing Code G2211: What Healthcare Providers Need to Know
The world of medical billing is complex, constantly evolving with new codes, regulations, and guidelines. Staying up-to-date is crucial for healthcare providers to ensure accurate and timely reimbursement for their services. One such code that has recently garnered significant attention is medical billing code G2211. This article delves deep into what G2211 is, its purpose, how it should be used, and the implications for healthcare practices. Understanding medical billing code G2211 is essential for optimizing revenue cycles and maintaining compliance. This comprehensive guide aims to provide clarity and actionable insights for navigating the intricacies of this important billing update.
What is Medical Billing Code G2211?
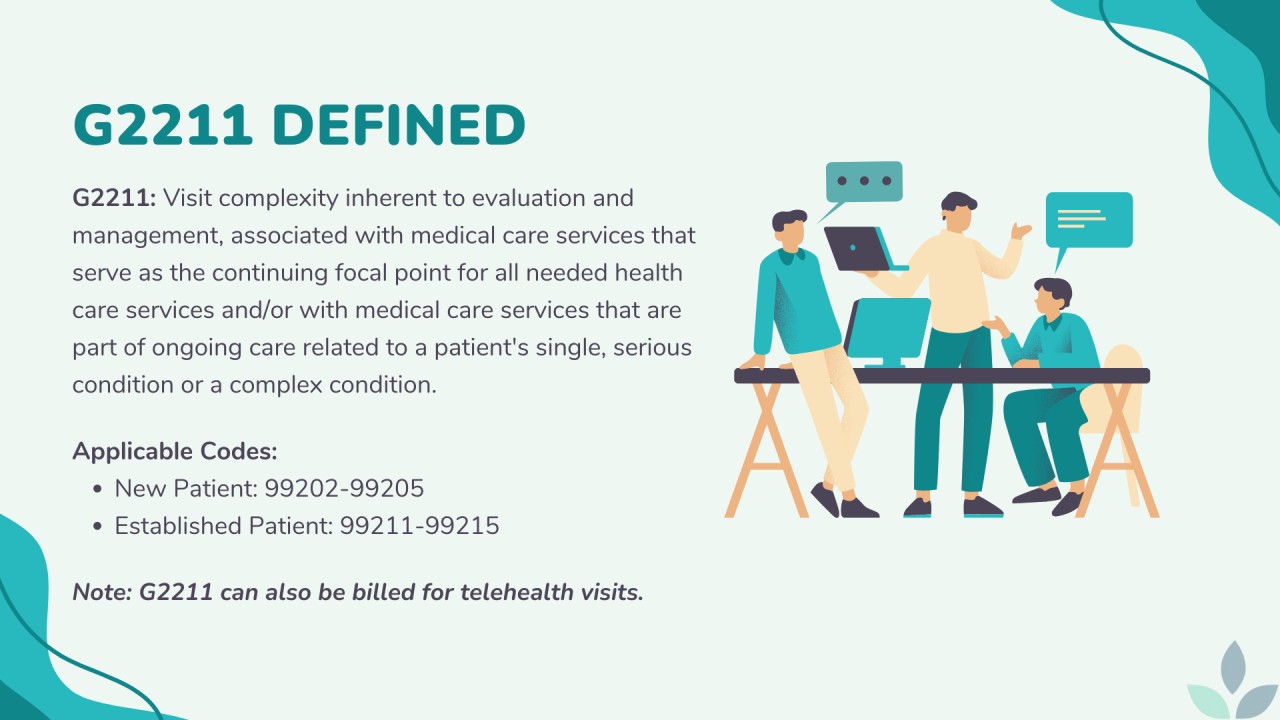
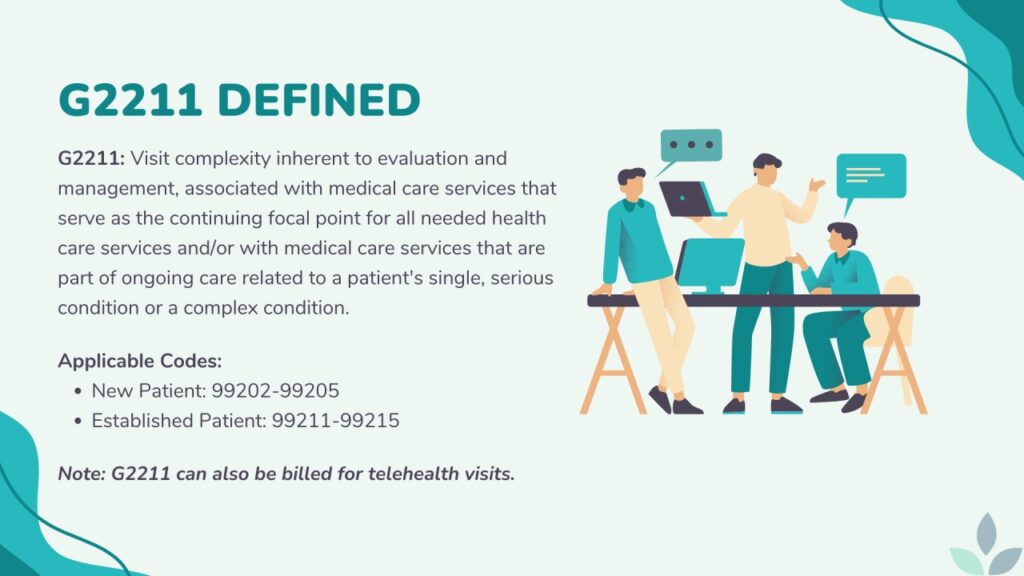
Medical billing code G2211, officially titled “Visit complexity inherent to evaluation and management associated with medical care services that serve as the continuing focal point for all needed health care services and/or with medical care services that are part of ongoing care related to a patient’s single, serious condition or a complex condition,” is an add-on code that can be used with certain evaluation and management (E/M) codes. It’s designed to recognize the additional resources and complexity involved when a provider serves as the continuing focal point for a patient’s care. Think of it as a way to acknowledge the extra time, effort, and expertise required to manage patients with complex or chronic conditions.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) introduced G2211 to better reflect the value of primary care and longitudinal care relationships. It aims to compensate physicians and other qualified healthcare professionals for the cognitive labor involved in managing patients over time, not just during a single visit. This is a shift towards recognizing the importance of continuity of care and the role of primary care providers in coordinating and managing patients’ overall health.
Who Can Use Medical Billing Code G2211?
G2211 isn’t for everyone. Its use is restricted to certain qualified healthcare professionals who have an established, ongoing relationship with the patient. This typically includes:
- Physicians (MD and DO)
- Nurse Practitioners (NP)
- Physician Assistants (PA)
- Clinical Nurse Specialists (CNS)
These providers must be the patient’s primary care provider or a specialist providing ongoing care for a single, serious, or complex condition. The code is not intended for use by providers who only see a patient for a one-time consultation or a limited number of visits. The key is the ongoing nature of the relationship and the provider’s role as a central point of contact for the patient’s healthcare needs.
When to Use Medical Billing Code G2211
The appropriate use of G2211 hinges on several factors. It’s crucial to understand the specific criteria outlined by CMS to ensure accurate billing and avoid potential audits. Here are some key considerations:
- Established Relationship: There must be an established and ongoing relationship between the provider and the patient. This implies the provider has seen the patient previously and is responsible for coordinating their care over time.
- Qualifying E/M Codes: G2211 can only be used in conjunction with specific office/outpatient E/M codes (99202-99215). It cannot be used with other types of E/M codes, such as those for hospital visits or emergency department services.
- Complexity and Continuity: The visit must involve medical care services that serve as the continuing focal point for all needed healthcare services and/or are part of ongoing care related to a patient’s single, serious condition or a complex condition. This means the provider is actively managing the patient’s overall health or a specific chronic illness.
- Not Just Routine Visits: G2211 is not intended to be used for every office visit. It should be reserved for visits where the provider spends significant time and effort coordinating care, managing complex medical issues, and addressing the patient’s overall health needs.
For example, a primary care physician managing a patient with diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease would likely be able to use G2211 during a comprehensive office visit where they review medications, discuss lifestyle modifications, and coordinate with specialists. However, a visit solely for a routine vaccination or a minor acute illness would likely not qualify.
How to Use Medical Billing Code G2211
Using G2211 correctly involves several steps:
- Determine Eligibility: First, confirm that the provider and the patient meet the criteria for using G2211, as outlined above.
- Select the Appropriate E/M Code: Choose the correct office/outpatient E/M code (99202-99215) that accurately reflects the level of service provided during the visit.
- Add G2211: Append G2211 to the chosen E/M code on the claim form.
- Documentation: Ensure that the medical record clearly documents the complexity of the patient’s condition, the provider’s role in coordinating care, and the medical necessity for using G2211. Detailed documentation is crucial in case of an audit.
Accurate coding requires a thorough understanding of the guidelines and careful attention to detail. It’s always a good practice to consult with a certified medical coder or billing specialist to ensure compliance and optimize reimbursement.
The Impact of Medical Billing Code G2211 on Healthcare Practices
The introduction of G2211 has significant implications for healthcare practices, particularly those focused on primary care and chronic disease management. Here are some key impacts:
- Increased Reimbursement: When used appropriately, G2211 can lead to increased reimbursement for qualifying office visits. This can help practices offset the costs associated with providing complex care and improve their financial stability.
- Recognition of Cognitive Labor: G2211 acknowledges the cognitive labor involved in managing patients with complex conditions. This is a positive step towards valuing the time and expertise of primary care providers and specialists who provide ongoing care.
- Emphasis on Continuity of Care: The code reinforces the importance of continuity of care and the role of primary care providers in coordinating and managing patients’ overall health. This can lead to improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs in the long run.
- Potential for Audits: The increased reimbursement potential also comes with a higher risk of audits. Practices must ensure they are using G2211 correctly and have adequate documentation to support their claims.
- Billing and Coding Challenges: The complexity of the code and the specific criteria for its use can create billing and coding challenges for practices. Proper training and education are essential to ensure accurate coding and avoid errors.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Medical Billing Code G2211
To ensure accurate billing and avoid potential penalties, it’s crucial to avoid common mistakes when using medical billing code G2211. Here are some pitfalls to watch out for:
- Using G2211 with Inappropriate E/M Codes: Remember, G2211 can only be used with specific office/outpatient E/M codes (99202-99215). Using it with other types of E/M codes is a common error.
- Applying G2211 to Every Visit: G2211 is not intended for routine visits. It should only be used when the visit involves significant complexity and the provider is actively managing the patient’s overall health or a specific chronic condition.
- Lack of Documentation: Insufficient documentation is a major red flag. The medical record must clearly document the complexity of the patient’s condition, the provider’s role in coordinating care, and the medical necessity for using G2211.
- Failing to Meet the Established Relationship Criteria: The provider must have an established and ongoing relationship with the patient. Using G2211 for a one-time consultation or a limited number of visits is inappropriate.
- Ignoring Payer-Specific Guidelines: While CMS provides the general guidelines for G2211, individual payers may have their own specific requirements. Always check with the payer to ensure compliance.
The Future of Medical Billing Codes Like G2211
The introduction of G2211 signals a broader trend towards recognizing the value of primary care and longitudinal care relationships in the healthcare system. As healthcare continues to evolve, we can expect to see more emphasis on value-based care and payment models that reward providers for delivering high-quality, coordinated care. This may lead to the development of new medical billing codes and reimbursement mechanisms that further incentivize these types of services.
Staying informed about these changes is crucial for healthcare providers to adapt to the evolving landscape and optimize their revenue cycles. This includes:
- Continuous Education: Participating in ongoing training and education programs to stay up-to-date on the latest coding and billing guidelines.
- Collaboration with Coding Experts: Working closely with certified medical coders and billing specialists to ensure accurate coding and compliance.
- Monitoring Payer Policies: Regularly reviewing payer policies and guidelines to stay informed about any changes or updates.
- Leveraging Technology: Utilizing technology solutions, such as electronic health records (EHRs) and billing software, to streamline the coding and billing process.
Conclusion
Medical billing code G2211 represents a significant step towards recognizing the value of primary care and longitudinal care relationships. By understanding its purpose, appropriate use, and implications, healthcare providers can optimize their revenue cycles, improve patient outcomes, and contribute to a more sustainable healthcare system. While navigating the complexities of medical billing can be challenging, staying informed and seeking expert guidance can help practices thrive in the ever-evolving healthcare landscape. Remember to always prioritize accurate documentation and adhere to payer-specific guidelines to ensure compliance and avoid potential penalties. [See also: Understanding E/M Coding Changes] [See also: Best Practices for Medical Billing] [See also: The Impact of Value-Based Care on Reimbursement]