How to Edit WordPress in HTML: A Comprehensive Guide
WordPress, the world’s most popular content management system (CMS), offers a user-friendly interface for creating and managing websites. However, sometimes you need to delve into the underlying code to achieve specific customizations or troubleshoot issues. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of how to edit WordPress in HTML, covering various methods, best practices, and potential pitfalls. Understanding how to edit WordPress in HTML can empower you to take full control of your website’s design and functionality.
Understanding the Basics: HTML, CSS, and WordPress
Before diving into the specifics of editing WordPress in HTML, it’s crucial to understand the relationship between HTML, CSS, and WordPress itself. HTML (HyperText Markup Language) forms the structural foundation of a webpage, defining elements like headings, paragraphs, images, and links. CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) controls the visual presentation of these elements, determining their colors, fonts, layout, and responsiveness. WordPress uses both HTML and CSS to create the overall look and feel of your website. While the WordPress dashboard provides a visual editor, sometimes direct HTML editing is necessary for more advanced customization.
Methods for Editing WordPress HTML
There are several ways to edit WordPress in HTML, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The best method depends on your technical skills and the specific task you’re trying to accomplish.
Using the WordPress Theme Editor
The built-in Theme Editor allows you to directly modify the HTML and CSS files of your active theme. This is a powerful tool, but it’s also the most risky. Any errors in your code can break your website. Always back up your theme before making changes.
- Navigate to Appearance > Theme Editor in your WordPress dashboard.
- Select the theme file you want to edit (e.g.,
header.php,footer.php,style.css). - Make your changes in the code editor.
- Click Update File to save your changes.
Caution: This method directly modifies your theme files. Always create a child theme before making any changes. A child theme allows you to modify the appearance of your site without directly altering the parent theme files. This is crucial for preserving your changes when the parent theme is updated.
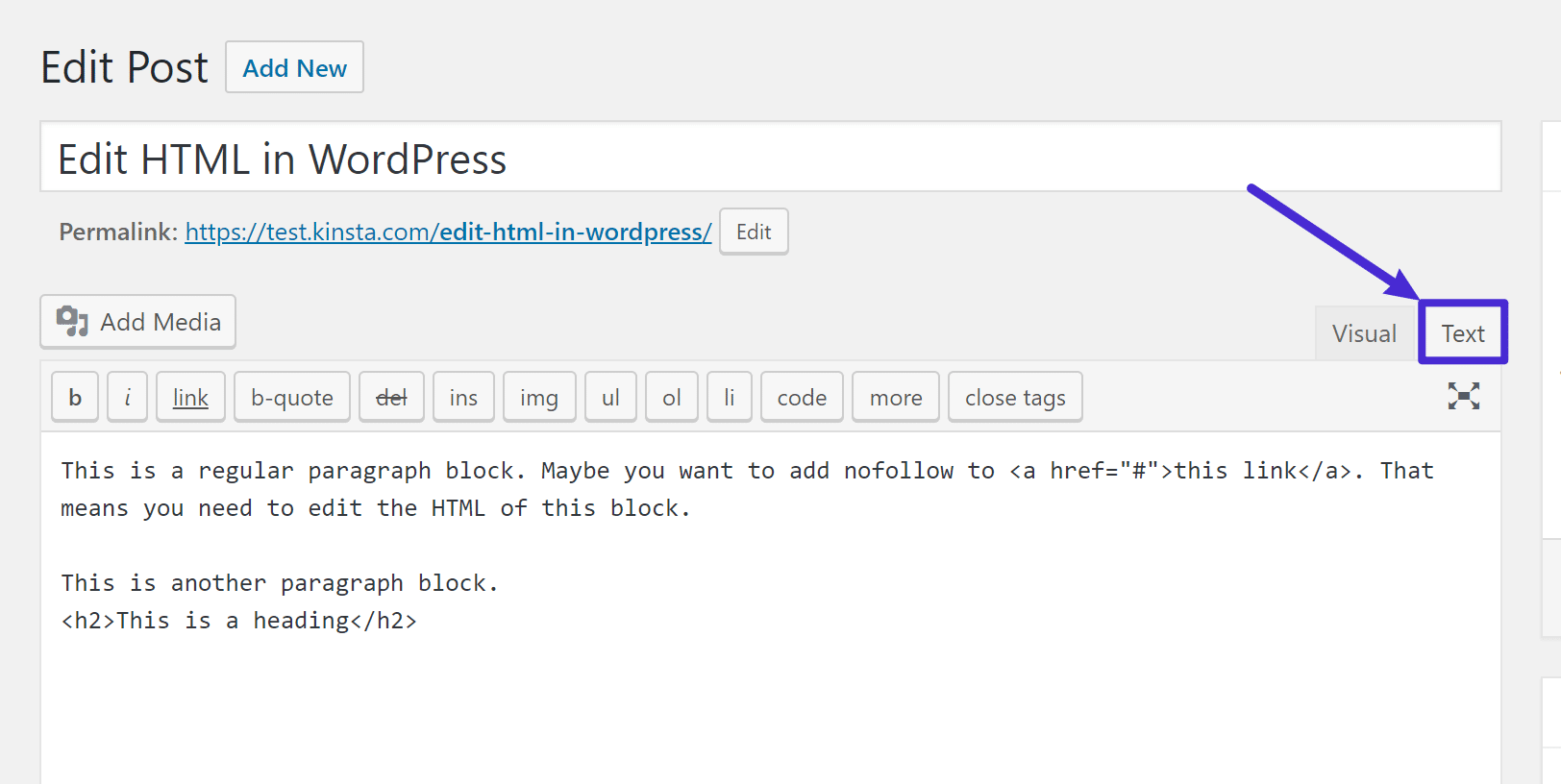
Editing HTML in WordPress Posts and Pages
The WordPress block editor (Gutenberg) allows you to add custom HTML blocks to your posts and pages. This is a safe and flexible way to add custom HTML without modifying your theme files.
- Open the post or page you want to edit.
- Click the + icon to add a new block.
- Search for the Custom HTML block.
- Enter your HTML code in the block.
- Click Update to save your changes.
Using a WordPress Plugin
Several WordPress plugins provide advanced HTML editing capabilities. These plugins often offer features like syntax highlighting, code completion, and error checking.
- Code Snippets: This plugin allows you to add custom code snippets to your website without modifying your theme files.
- Insert Headers and Footers: This plugin allows you to add code to the
<head>and<body>sections of your website. - Advanced Custom Fields (ACF): While not solely for HTML editing, ACF allows you to create custom fields that can be used to display HTML content.
Accessing WordPress Files via FTP/SFTP
For more advanced customization, you can access your WordPress files directly via FTP (File Transfer Protocol) or SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol). This allows you to edit any file on your server, including theme files, plugin files, and WordPress core files.
- Connect to your server using an FTP/SFTP client (e.g., FileZilla, Cyberduck).
- Navigate to the
wp-contentdirectory. - Locate the theme or plugin you want to edit.
- Download the file you want to edit to your computer.
- Edit the file using a text editor (e.g., Notepad++, Sublime Text, VS Code).
- Upload the modified file back to your server, overwriting the original file.
Important: Editing files directly via FTP/SFTP requires a good understanding of HTML, CSS, and WordPress file structure. Always back up your files before making any changes.
Best Practices for Editing WordPress in HTML
When you edit WordPress in HTML, it’s crucial to follow best practices to avoid breaking your website and ensure your changes are maintainable.
- Always Back Up Your Website: Before making any changes to your WordPress files, create a complete backup of your website. This includes your database, theme files, plugin files, and uploads.
- Use a Child Theme: When modifying theme files, always use a child theme. This will prevent your changes from being overwritten when the parent theme is updated.
- Validate Your Code: Use an HTML validator to check your code for errors before saving your changes.
- Test Your Changes Thoroughly: After making changes, test your website thoroughly to ensure everything is working as expected.
- Use Code Comments: Add comments to your code to explain what each section does. This will make it easier to understand and maintain your code in the future.
- Minify Your Code: Minifying your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files can improve your website’s performance.
- Keep Your Code Organized: Use proper indentation and spacing to make your code more readable.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When you edit WordPress in HTML, there are several common mistakes to avoid:
- Editing the Core WordPress Files: Never edit the core WordPress files. These files are updated regularly, and any changes you make will be overwritten.
- Forgetting to Close HTML Tags: Forgetting to close HTML tags can break your website’s layout.
- Using Inline Styles: Avoid using inline styles (e.g.,
<p style="color: red;">). Instead, use CSS classes and styles in your theme’s stylesheet. - Not Testing on Different Browsers and Devices: Always test your changes on different browsers and devices to ensure your website looks good on all platforms.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If you encounter problems after editing WordPress in HTML, here are some common troubleshooting steps:
- Check Your Error Logs: Your server’s error logs can provide valuable information about what went wrong.
- Disable Your Plugins: Sometimes, plugin conflicts can cause issues. Try disabling your plugins one by one to see if that resolves the problem.
- Revert to a Previous Backup: If you have a backup of your website, revert to that backup to restore your website to a working state.
- Consult the WordPress Codex: The WordPress Codex is a comprehensive online manual for WordPress. It contains detailed information about all aspects of WordPress.
Conclusion
Learning how to edit WordPress in HTML is a valuable skill for any WordPress user. Whether you’re making minor tweaks to your theme or creating complex custom layouts, understanding HTML can empower you to take full control of your website. By following the best practices outlined in this guide and avoiding common mistakes, you can safely and effectively edit WordPress in HTML to create a website that meets your specific needs.
Remember to always back up your website before making any changes and use a child theme when modifying theme files. With a little practice and patience, you can master the art of editing WordPress in HTML and create a truly unique and professional website. Understanding how to edit WordPress in HTML is crucial for advanced customization and troubleshooting. By following the steps and best practices outlined above, you can confidently modify your WordPress website’s HTML and achieve your desired results. This knowledge empowers you to fine-tune your site’s appearance and functionality beyond the limitations of the visual editor. Further, knowing how to edit WordPress in HTML allows for optimization beyond the standard WordPress interface.
[See also: WordPress Theme Customization Tips]
[See also: Best WordPress Plugins for Developers]
[See also: Troubleshooting WordPress Errors]